#
DISPLAYING information from an Oracle database
This tutorial explains to you how we can display data from an Oracle database using a Thymeleaf application.
In order to display rows using a Thymeleaf template, you have to create a Hello World example with SpringBoot and Thymeleaf (this is my case).
After that you have to define an interface for creating the session and its implementation:
package com.myproject.hibernate;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
public interface DbConnection {
SessionFactory getSessionFactory();
}package com.myproject.hibernate;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Environment;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.myproject.models.Emp;
import com.myproject.models.Pozitii;
@Service
@Profile("prod")
public class ProdHibernateUtil implements DbConnection{
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
@Override
public SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if (sessionFactory == null) {
try {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// Hibernate settings equivalent to hibernate.cfg.xml's properties
Properties settings = new Properties();
settings.put(Environment.DRIVER, "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
settings.put(Environment.URL, "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db11g");
settings.put(Environment.USER, "proiect");
settings.put(Environment.PASS, "1");
settings.put(Environment.DIALECT, "org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect");
settings.put(Environment.SHOW_SQL, "true");
configuration.setProperties(settings);
configuration.addAnnotatedClass(Pozitii.class);
configuration.addAnnotatedClass(Emp.class);
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder()
.applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sessionFactory;
}
}Info
As you can see, this class creates a session to an Oracle database. Also, you can use profiles or not. In this case I use a profile. If you are not using profiles, the interface is not needed.
Also, you need to create a class for mapping the database table:
package com.myproject.models;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "Emp")
public class Emp {
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "telephone")
private String telephone;
@Column(name = "salary")
private String salary;
//id
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
//name
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//telephone
public String getTelephone() {
return telephone;
}
public void setTelephone(String telephone) {
this.telephone = telephone;
}
//salary
public String getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(String salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}Also, you need to create the DAO (Data Access Object) class for that table. In this case you only SELECT data, but in real live you have all the operations (select, insert, update, delete) almost any time.
package com.myproject.dao;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.myproject.hibernate.DbConnection;
import com.myproject.hibernate.ProdHibernateUtil;
import com.myproject.models.Emp;
@Repository
public class EmpDao {
@Autowired
private DbConnection dbConnection;
public List<emp> getEmp() {
try (Session session = dbConnection.getSessionFactory().openSession()) {
return session.createQuery("from Emp", Emp.class).list();
}
}
}Here it is the Controller class for my application:
package com.myproject;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.myproject.dao.*;
import com.myproject.models.*;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@Autowired
private EmpDao empDao;
//EMP
@RequestMapping("/emp")
public String emp(Map<string, object=""> model) {
List<emp> emp = empDao.getEmp();
model.put("emp", emp);
return "emp";
}
}Here it is the Thymeleaf template used for the View part of the MVC:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./css/bootstrap.min.css">
<title>Employees</title>
<style>
div.mytable {
margin: auto;
width: 1020px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="mytable">
<nav aria-label="breadcrumb">
<ol class="breadcrumb">
<li class="breadcrumb-item"><a href="/">Home</a></li>
<li class="breadcrumb-item active" aria-current="page">Employees</li>
</ol>
</nav>
</div>
<table class="table table-striped table-primary">
<thead class="ttop">
<tr class="table-info">
<td width="20px"><b> ID</b></td>
<td><b>NAME</b> </td>
<td><b>TELEPHONE</b> </td>
<td><b>SALARY</b> </td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="empl, iStat : ${emp}" th:style="${iStat.odd}? 'font-weight: normal;'">
<td width="20px" th:text="${empl.id}">
</td><td th:text="${empl.name}">
</td><td th:text="${empl.telephone}">
</td><td th:text="${empl.salary}">
</td></tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>The profile is set when the application starts:
package com.myproject;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.core.env.AbstractEnvironment;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySpringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty(AbstractEnvironment.ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME, "prod");
SpringApplication.run(MySpringApplication.class, args);
}
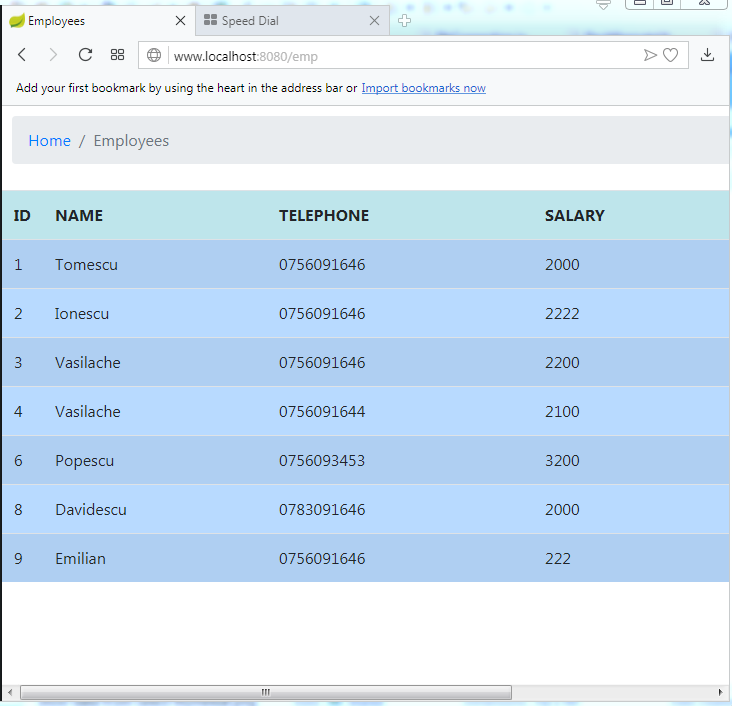
}And here it is the web page when you run the application:
Info
This application uses Hibernate and for this reason, you have to add the following in pom.xml :